
The higher a product’s contribution margin and contribution margin ratio, the more it adds to its overall profit. In the same case, if you sell 100 units of the product, then contributing margin on total revenue is $6,000 ($10,000-$4,000). In short, profit margin gives you a general idea of how well a business is doing, while contribution margin helps you pinpoint which products are the most profitable. Fixed costs are often considered sunk costs that once spent cannot be recovered. These cost components should not be considered while making decisions about cost analysis or profitability measures.
- Contribution margin (CM) is a financial measure of sales revenue minus variable costs (changing with volume of activity).
- You can even calculate the contribution margin ratio, which expresses the contribution margin as a percentage of your revenue.
- When comparing the two statements, take note of what changed and what remained the same from April to May.
- It is an important input in calculation of breakeven point, i.e. the sales level (in units and/or dollars) at which a company makes zero profit.
How to calculate a contribution margin
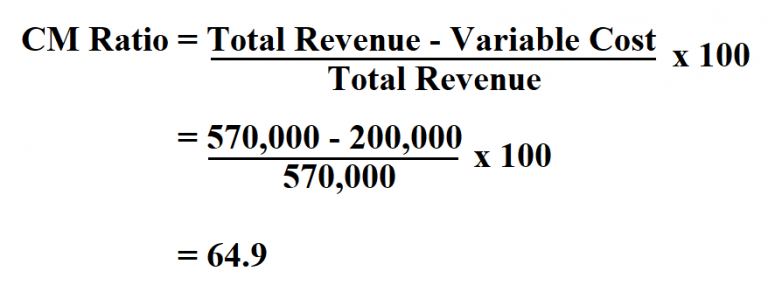
A contribution margin analysis can be done for an entire company, single departments, a product line, or even a single unit by following a simple formula. The contribution margin can be presented in dollars or as a percentage. With a high contribution margin ratio, a firm makes greater profits when sales increase and more losses when sales decrease compared to a firm with a low ratio. The contribution margin (CM) is the amount of revenue in excess of variable costs. Therefore, the contribution margin reflects how much revenue exceeds the coinciding variable costs.
What is your current financial priority?
Managerial accountants also use the contribution margin ratio to calculate break-even points in the break-even analysis. Management should also use different variations of the CM formula to analyze departments and product lines on a trending basis like the following. Soundarya Jayaraman is a Content Marketing Specialist at G2, focusing on cybersecurity. Formerly a reporter, Soundarya now covers the evolving cybersecurity landscape, how it affects businesses and individuals, and how technology can help.
Operating Assumptions
Cost accountants, financial analysts, and the company’s management team should use the contribution margin formula. CM is used to measure product profitability, set selling prices, decide whether to introduce a new product, discontinue selling a specific product, or accept potential customer orders with non-standard pricing. Calculating contribution margin (the difference between sales revenue and variable costs) is an effective financial analysis tool for making strategic business decisions. Weighted average contribution margin per unit equals the sum of contribution margins of all products divided by total units. Weighted average contribution margin ratio equals the sum of contribution margins of all products divided by total sales.
Contribution Margin Ratio: What It Is and How to Calculate It
Variable costs vary with the volume of activity, such as the number of units of a product produced in a manufacturing company. Jump, Inc. is a sports footwear startup which currently sells just one shoe brand, A. The sales price is $80, variable costs per unit is $50 and fixed costs are $2,400,000 per annum (25% of the which are manufacturing overhead costs) . Contribution margin ratio is a calculation of how much revenue your business generates from selling its products or services, once the variable costs involved in producing and delivering them are paid. This can be a valuable tool for understanding how to price your products to ensure your business can pay its fixed costs, such as salaries and office rent, and still generate a profit. The break even point (BEP) is the number of units at which total revenue (selling price per unit) equals total cost (fixed costs + variable cost).
When the contribution margin is calculated on a per unit basis, it is referred to as the contribution margin per unit or unit contribution margin. For example, assume that the students are going to lease vans from their university’s motor pool to drive to their conference. A university van will hold eight passengers, at a cost of $200 per van. If they send one to eight participants, the fixed cost for the van would be $200. If they send nine to sixteen students, the fixed cost would be $400 because they will need two vans. We would consider the relevant range to be between one and eight passengers, and the fixed cost in this range would be $200.
Investopedia contributors come from a range of backgrounds, and over 25 years whitepapers on accounting and cloud technology there have been thousands of expert writers and editors who have contributed.
The best contribution margin is 100%, so the closer the contribution margin is to 100%, the better. The higher the number, the better a company is at covering its overhead costs with money on hand. The contribution margin ratio is calculated as (Revenue – Variable Costs) / Revenue. Now, divide the total contribution margin by the number of units sold. Calculating the contribution margin for each product is one solution to business and accounting problems arising from not doing enough financial analysis. Calculating your contribution margin helps you find valuable business solutions through decision-support analysis.
If total fixed cost is $466,000, the selling price per unit is $8.00, and the variable cost per unit is $4.95, then the contribution margin per unit is $3.05. The break-even point in units is calculated as $466,000 divided by $3.05, which equals a breakeven point in units of 152,787 units. Contribution margin (sales revenue minus variable costs) is used to evaluate, add and remove products from a company’s product line and make pricing and sales decisions. Management accountants identify financial statement costs and expenses into variable and fixed classifications.
Thus, CM is the variable expense plus profit which will incur if any activity takes place over and above BEP. Regardless of how contribution margin is expressed, it provides critical information for managers. Understanding how each product, good, or service contributes to the organization’s profitability allows managers to make decisions such as which product lines they should expand or which might be discontinued.